
Modern volumetric capnographs incorporate this physiologic approach, enabling intensivists to measure VD/VTphys at the bedside. Currently, dead space is measured at the bedside by volumetric capnography, which reports expired CO 2 elimination as a function of expired VT, and VD/VTphys is calculated using the Enghoff’s modification of Bohr’s original equation: VD/VTphys = (PaCO 2 – PECO 2)/PaCO 2, where PaCO 2 is the arterial partial pressure of CO 2 obtained by arterial blood sampling and PECO 2 is an estimate of mixed expired partial pressure of CO 2 obtained from the mid-portion of phase III of the volumetric capnogram.

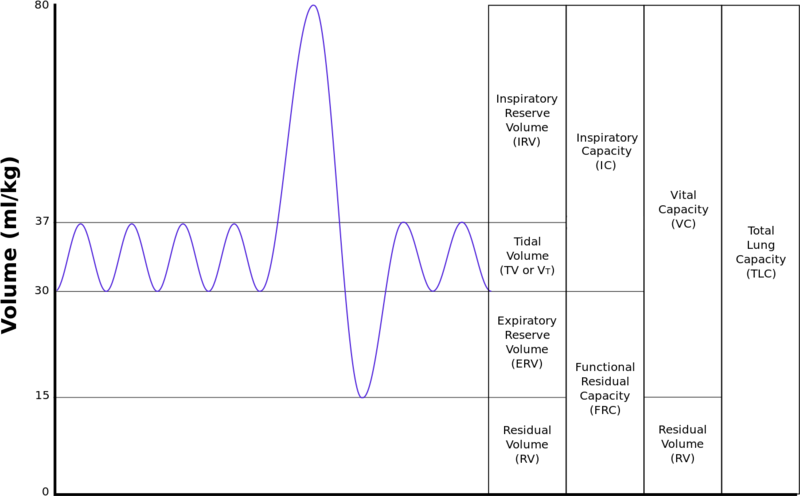
The physiologic ventilatory dead space fraction (VD/VTphys) is usually defined as the fraction of tidal volume (VT) that does not participate in gas exchange.

Dead space comprises two separate components: airway dead space (the volume of areas that do not contribute to gas exchange) and alveolar dead space (the volume of well-ventilated alveoli that receive minimal blood flow). However, differences in the exact way of measuring this space result in clinically significant different results and, therefore, debate remains about the true value of this measured parameter.Ĭopyright © 2023, StatPearls Publishing LLC.Dead space refers to lung areas that are ventilated but not perfused. Indeed, it may serve as a prognostic factor in patients with acute repository distress syndrome (ARDS) who require ventilation. This phenomenon has clinical significance because, both in healthy and impaired lungs, properly calculating and accounting for this non-physiological space is important for the proper respiratory care of ventilated patients. This is therefore termed anatomical dead space as it serves no respiratory function. Anatomic dead space is an important phenomenon in respiratory physiology whereby, owing to the fact that upper airways do not function as locations for gas exchange, and because of the tidal nature of ventilation, there is always a fraction of the inspired air that does not perform a physiologic function of exchanging carbon dioxide for oxygen.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
